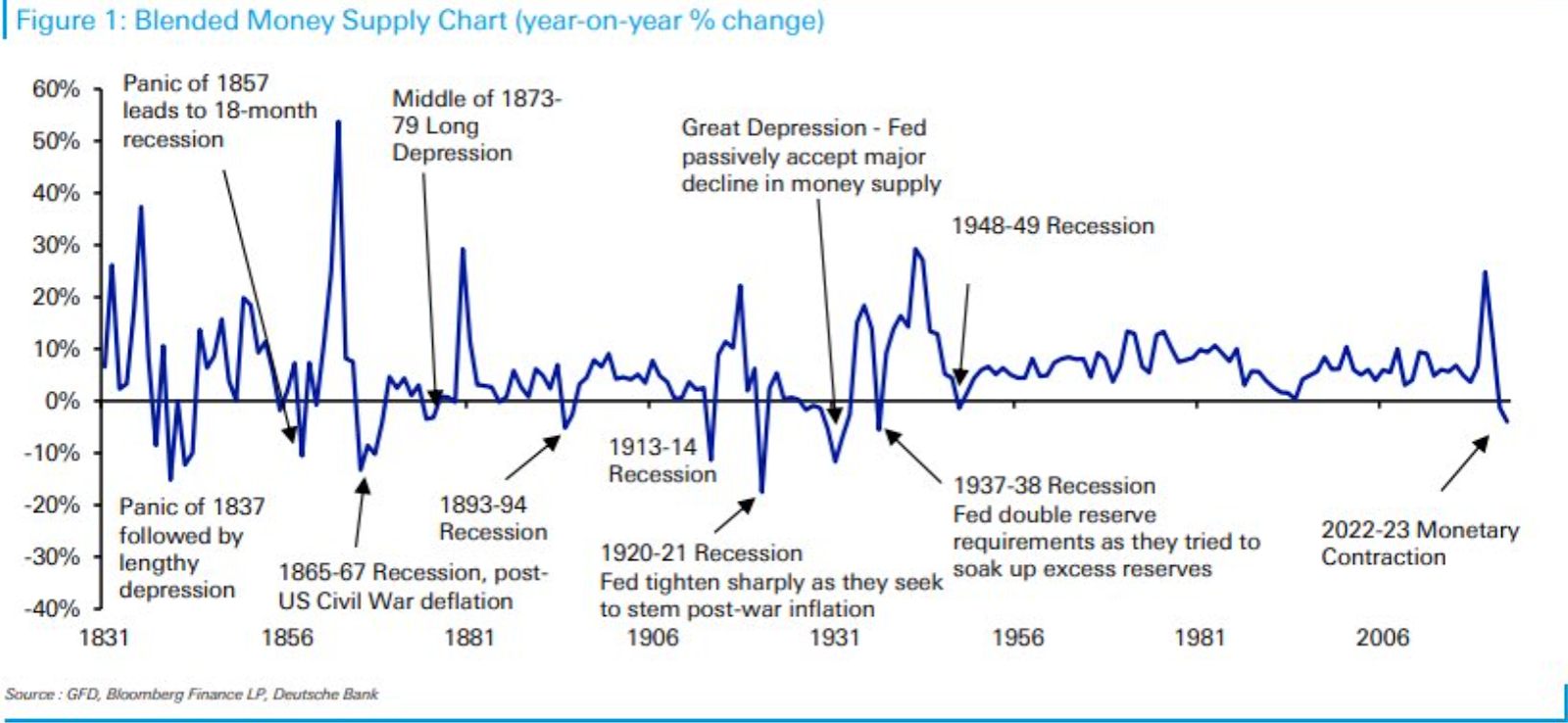
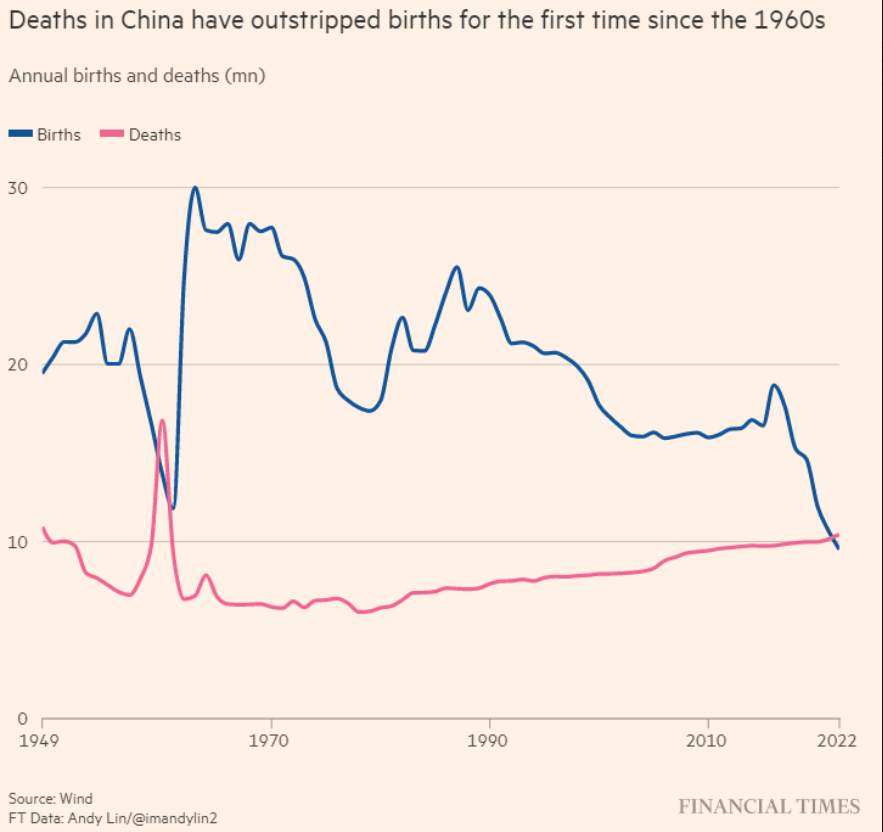
Comments regarding Musk’s Twitter ownership - from ChatGPT
The ownership structure of a platform like Twitter can have
several social implications, whether it is privately owned or publicly owned.
Here are some key considerations:
Privately
Owned:
1.
Concentration of Power: When a platform like Twitter is
privately owned, all decision-making authority rests with the owners or the
company's leadership. This concentration of power can lead to concerns about
accountability, transparency, and potential biases in content moderation and
platform policies.
2.
Profit Motive: Private ownership often means the primary goal of
the company is to generate profit for its owners or shareholders. This can
impact the platform's priorities and decision-making, as profit considerations
may take precedence over other social or public interest concerns.
3.
User Rights and Control: Private ownership gives the company
significant control over user data and platform policies. This can raise
concerns about privacy, data security, and censorship. The company may have the
discretion to enforce certain rules and restrictions on user behavior,
potentially affecting freedom of speech and expression.
4.
Innovation and Responsiveness: Privately owned platforms may be
more agile and responsive to market demands, allowing them to innovate and
adapt quickly. However, their actions may be driven by profit motives rather
than broader social or public interests.
Publicly
Owned:
1.
Public Accountability: Publicly owned platforms may be subject
to greater scrutiny and accountability, as they are answerable to a wider range
of stakeholders, including government bodies, regulatory authorities, and the
general public. This accountability can help ensure more transparent
decision-making and protection of user rights.
2.
Democratic Participation: Public ownership may provide
opportunities for more democratic participation in platform governance.
Publicly owned platforms could potentially involve users, experts, and public
representatives in decision-making processes, fostering diverse perspectives
and collective decision-making.
3.
Public Interest Focus: Publicly owned platforms can prioritize
public interest goals and societal well-being over short-term profit motives.
This could include considerations such as promoting freedom of expression,
addressing misinformation, and protecting user privacy, with a greater emphasis
on the common good.
4.
Potential for Political Influence: Public ownership can
introduce political dynamics and government influence into platform operations.
This may raise concerns about political interference, censorship, or biased
content moderation decisions. Striking the right balance between independence
and government oversight is crucial.
It is
important to note that the actual social implications can vary depending on
various factors, such as the specific ownership structure, legal frameworks,
and the company's approach to governance and decision-making.